Heat loss
The loss heat in the motor, which results from the power loss PV, has to be dissipated. The power loss is calculated as follows:
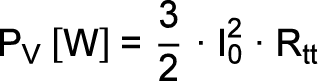
| I0: |
Continuous standstill current as per the motor data sheet |
| Rtt: |
Terminal resistance as per the motor data sheet |
In the case of liquid-cooled motors, the amount of power loss that can be dissipated is proportional to the flow rate of the coolant. The minimum coolant flow rate per time unit is calculated as follows:
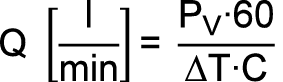
| ΔT |
Permissible coolant temperature increase between the supply line and return line: ΔT < 5 °K |
| C: |
Specific heat capacity of the cooling medium, e.g. water: 4187 J/(kg·K) |
Furthermore, AMK specifies minimum flow rates for the various motor sizes: Siehe 'Liquid cooling'.
