Safe operating stop (SOS)
Properties
- Safety function according to DIN EN 61800-5-2:2008-04
- Safe standstill monitoring with drift recognition
(2-channel monitoring of the speed and position feedback value)
Description
The safety function can be started by a safe input or by the corresponding bit in the control data.
The acknowledgement can be fed back by safe output or by status data.
The started SOS safety function monitors the actual speed value and monitors the compliance with the safe speed standstill window and the safe position standstill window.
|
|
|
|
|
Danger to life due to unexpected movements! The normal operating function 'Safe encoder monitoring (SEM)' is active at any time. In the status 'Safe torque off (STO)', in case of mains failure or defective drive controller, the drive will be torque-free. External force applied to the drive axis can cause life-threatening movements, e.g. hanging axes can fall down. Steps to prevent:
|
Example 1: Drive movement meets the permissible range of movement
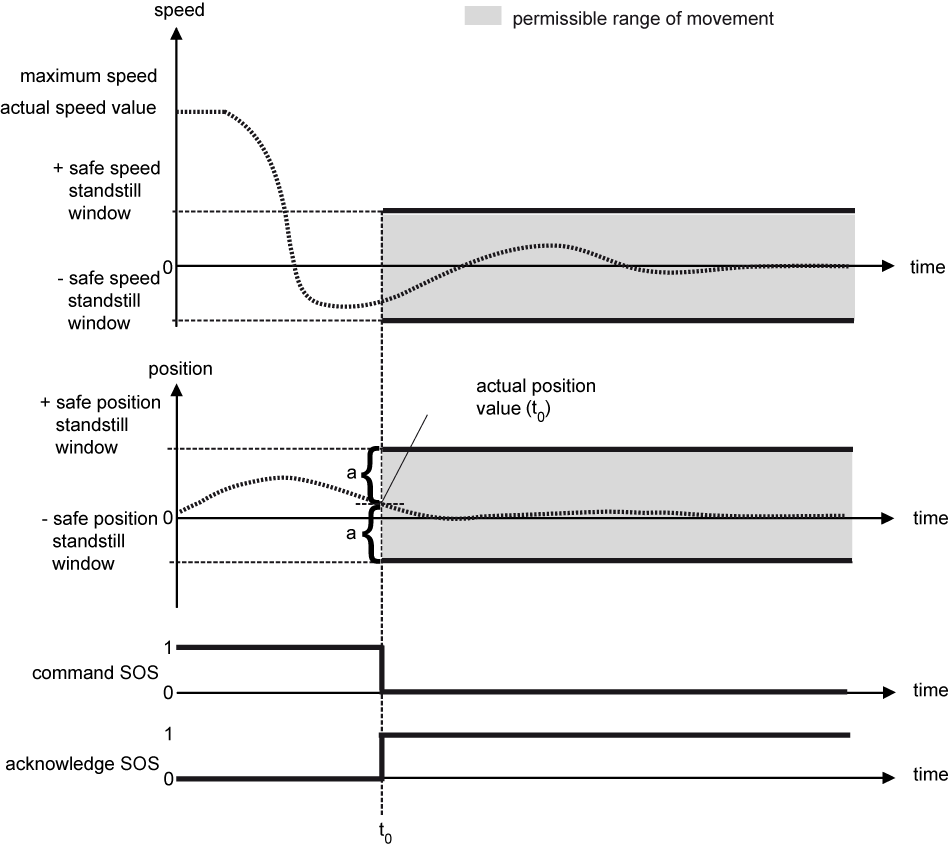
|
Time t |
Explanation |
|---|---|
|
t = t0 |
The safety function is started. The safe position standstill window is symmetrically placed around the position feedback value of the drive at the time of the commanding. |
Reaction in case of an error
As soon as the safety function detects a deviation from the limits of the monitored values, the drive is set to the safe state 'Safe torque off (STO)' (example 2) and (example 3).
|
|
|
|
|
Danger to life due to unexpected movements! The drive will be torque-free in the status 'Safe torque off (STO)', in case of mains failure or in case of faulty drive controller. External application of force on the drive axis may result in life-threatening movements (e.g. hanging axes can fall down). Steps to prevent:
|
Example 2: Drive movement deviates from the safe speed standstill window
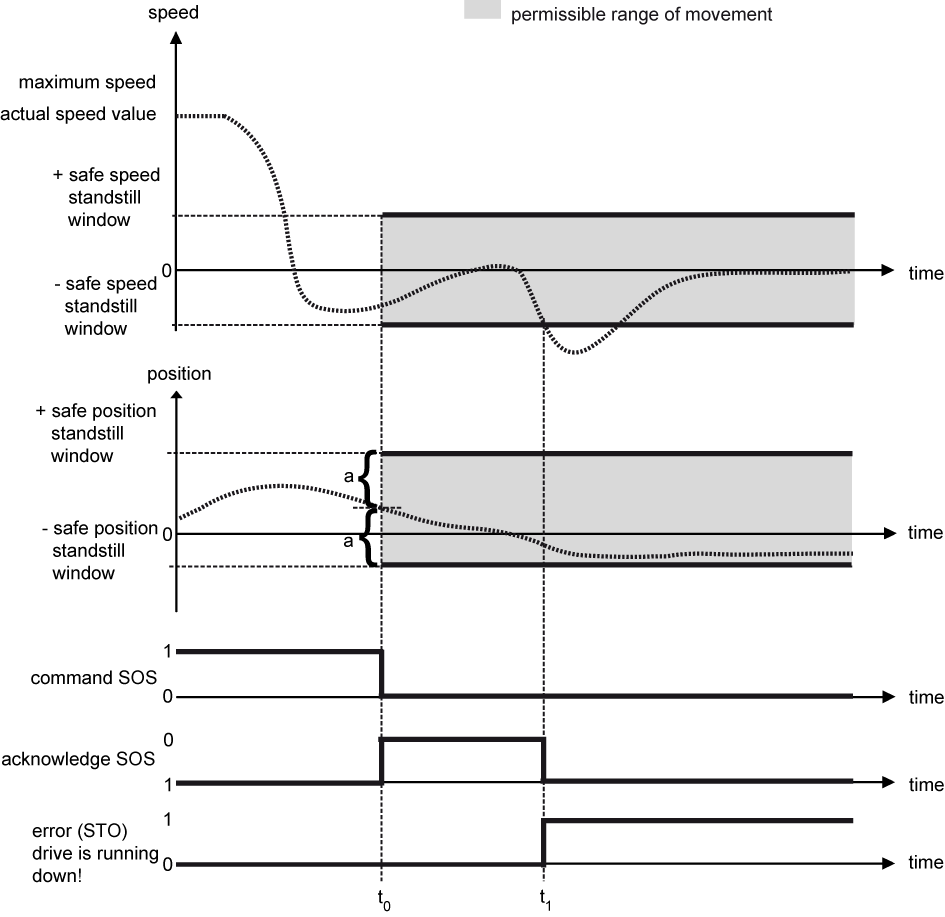
|
Time t |
Explanation |
|---|---|
| t = t0 |
The safety function is started. The safe position standstill window is symmetrically placed around the position feedback value of the drive at the time of the commanding. |
|
t0 < t < t1 |
The safety function monitors the compliance with the safe speed standstill window and the safe position standstill window and checks whether the actual speed value meets the permissible range of movement. |
|
t = t1 |
The safety function detects that the safe speed standstill window has been left, switches the drive into the STO state and sets the error bit. The SOS acknowledgement bit is reset. |
|
t ≥ t1 |
In the STO state, drive movements are no longer monitored since no further error reaction is possible. |
Example 3: Drive movement deviates from the safe position standstill window
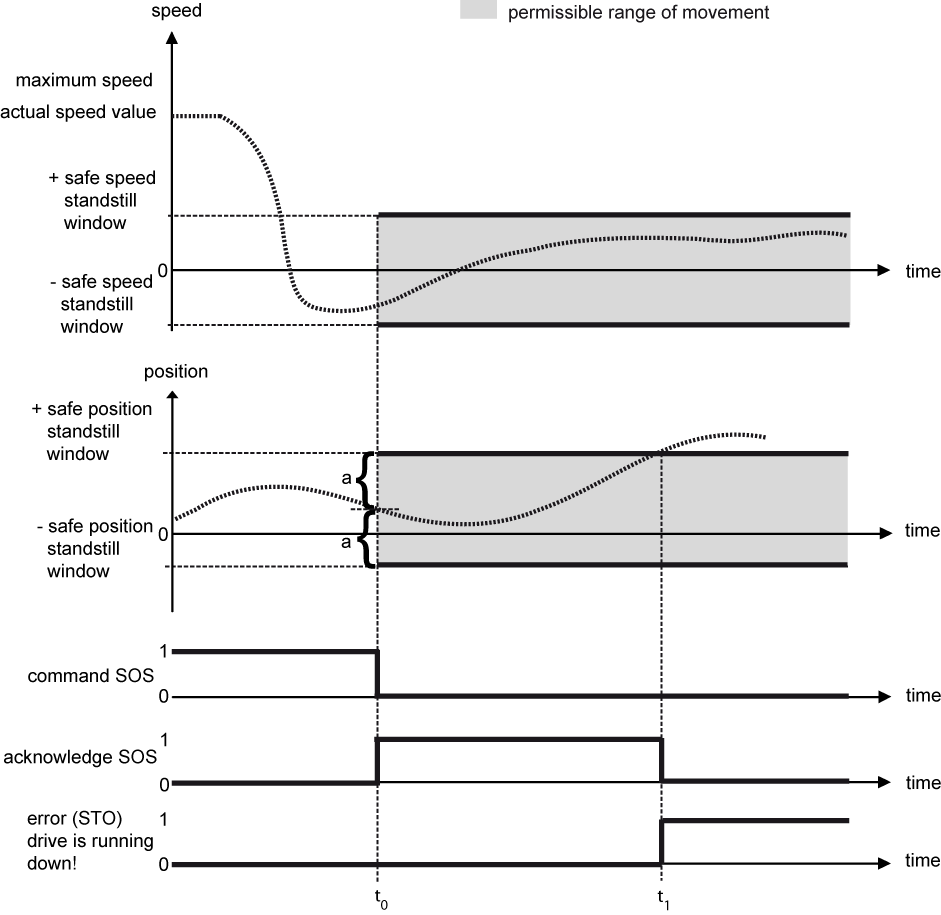
|
Time t |
Explanation |
|---|---|
| t = t0 |
The safety function is started. The safe position standstill window is symmetrically placed around the position feedback value of the drive at the time of the commanding. |
|
t0 < t < t1 |
The safety function monitors the compliance with the safe speed standstill window and the safe position standstill window and checks whether the actual speed value meets the permissible range of movement. |
|
t = t1 |
The safety function detects that the positions standstill window has been left, switches the drive into the STO state and sets the error bit. The SOS acknowledgement bit is reset. |
|
t ≥ t1 |
In the STO state, drive movements are no longer monitored since no further error reaction is possible. |
Acknowledge an error with "Clear error"
As soon as an active safety function detects a deviation from the limits of the monitored values, the drive is set to the intended stop function. The error bit (FSoE status bit 7) is set and the acknowledgment of the safe status is withdrawn.
With the 'Clear error' signal (FSoE control bit 7 or the 'Clear error' command in the drive controller) the
error status ist acknowledged (deleted). If during and after the 'Clear error' the start signal from a previous safety function is still active and no other changes to the settings of the safety function have been made, the safety function restarts and also transition times (if available) work again.
Parameters


